-
Automated Learning Academy
Thank you for choosing Automated Learning!
If you are interested in purchasing access to one of our courses, you may purchase access at AutomatedLearning.com. You may also reach out to sales@automatedlearning.com for volume discounts and current pricing.
Current customers may click here to login.
After logging in, you will find your assigned courses on the left side under "My Courses". If at any point you have difficulties, please reach out to our support team and we will be more than happy to assist at the below email address:
Available courses

This comprehensive interactive multimedia program is designed as an introduction to principals of Electrostatic Discharge. It is intended for all personnel including managers, operators, assemblers, technicians, engineers, and trainers. The program has two modules, with a test keyed to content:
- Introduction (approximately 20 minutes)
- What is ESD? (approximately 20 minutes)
Test (approximately 30 minutes)
The course can be taken in several sessions. You can leave and later resume modules of the course at any point.

A comprehensive interactive multimedia learning program with certification for those who work with static sensitive devices. The training is directed to assemblers and support personnel.
This course is divided into two modular sections and a test:
-
ESD Controls (approximately 30 minutes)
-
Personal Grounding (approximately 30 minutes)
-
Test (approximately 30 minutes)
Participants can leave and later resume modules of the course at any point.

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Explain conditions most likely to cause uncontrolled electrostatic discharge
-
Identify three types of ESD protective packaging
-
Explain the use of ionization and topical antistats for static control
-
Describe the impact of environmental factors on static charge
-
Describe the requirements of an ESD protective workstation
-
Describe the function of ESD protective items in a protected area
-
Describe the correct use of ESD protective smocks, wrist straps, and footwear
-
Recognize correct use of personal protection around high voltage hazards
-
List recommended ESD protective practices at workstations
Participants successfully completing the training course will be able to:
- Describe what static electricity is, how it is produced, and how uncontrolled discharge can damage components and equipment.
- Explain the Human Body Model (HBM) of ESD damage
- Identify correct procedures for controlling HBM related ESD
- Explain the Charged Device Model (CDM) of ESD damage
- Identify correct procedures for controlling CDM related ESD
- Describe safe and unsafe practice in handling devices and assemblies
Participants successfully completing the program will gain knowledge required to:
- describe the characteristics of field service environments that could result in ESD failures.
- describe the recommended ESD Field Kit.
- describe the procedures for setting up a temporary ESDPA in the field.
- describe the procedures for working inside the ESDPA in the field.

The objectives of this course are for the participant to:
- describe the importance of ESD control and identify the roles and responsibilities of management, program coordinators, and supervisors.
- describe the ESD control program plan.
- describe the ESD audit plan.
- describe the steps necessary to maintain an ESD culture.
Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Describe what static electricity is, how it is produced, and how its uncontrolled discharge can damage components and equipment
-
Explain the Human Body Model (HMB) of ESD damage
-
Identify correct procedures for controlling ESD caused by the HBM
-
Describe the wrist strap as a critical component in HBM ESD control
-
Describe how, where and when a wrist should be tested
-
Explain the Charged Device Model (CDM) of ESD damage
-
Identify correct procedures for controlling ESD caused by the Charged Device Model
-
Describe safe and unsafe practice in handling assemblies
Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Industry trends driving increased use of highly-sensitive ESD class 0 components
-
The leading cause of ESD failures in the electronics industry today
-
Critical factors in a total control system approach for ESD class 0
-
The shift in thinking required about control methods for ESD class 0
-
The limitations of conventional ESD control methods with examples
-
Examples of mitigation techniques to control ESD class zero risks
-
The key issue of Charged Device Model ESD failure for class 0
-
The critical change in ESD control design for class zero
-
Additional requirements of ESD control in a cleanroom environment
-
The impact of class 0 requirements on ESD audit metrics
-
ESD metrics as management tools
-
ESD metrics as management tools
-
A ten step process in manufacturing to become class zero ready
-
The time and effort required to develop a robust ESD class 0 system

Un programme d'apprentissage multimédia interactif complet avec certification pour ceux qui travaillent avec des appareils sensibles à l'électricité statique. Ce cours initie le stagiaire aux décharges électrostatiques. La formation s'adresse aux assembleurs et au personnel de soutien.
Un programme d'apprentissage multimédia interactif complet avec certification pour ceux qui travaillent avec des appareils sensibles à l'électricité statique. La formation s'adresse aux assembleurs et au personnel de soutien.

Un completo programa de aprendizaje multimedia interactivo con certificación para quienes trabajan con dispositivos sensibles a la estática. Este curso introduce al alumno a las descargas electrostáticas. La capacitación está dirigida a ensambladores y personal de apoyo.
Un programa de aprendizaje multimedia interactivo completo con certificación para aquellos que trabajan con aparatos sensibles a la electricidad estática. La formación está dirigida a los ensambladores y al personal de apoyo.

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Identify hazardous energy as a workplace danger
-
Describe common forms of energy and hazardous energy in the workplace
-
Explain components of a hazardous energy control program
-
Explain government regulations relating to Lockout/Tagout
-
Identify Lockout as the primary procedure in hazardous energy control
-
Explain when Lockout should be implemented
-
Explain why Lockout is important in the workplace
-
Describe seven unique steps in a Lockout procedure
-
Describe group Lockout and correct Lockout scenario
-
Explain the roles and responsibilities of personnel in the workplace
-
Explain who has authorization to perform Lockout
-
Describe the impact and importance of visible communication
-
identify tagout as having a supporting role in hazardous energy control
-
Explain how Tagout differs from Lockout
-
Describe the Tagout process
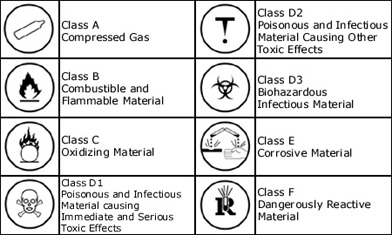
This comprehensive interactive multimedia program is intended for all employees who need an introduction to WHMIS labeling standards and requirements, Material Safety Data Sheets, and basic emergency procedures.
Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Describe the function of WHMIS, and relate each WHMIS symbol to the specific class of hazard it represents.
-
Differentiate between the different types of labels.
-
Explain the routes of entry.
-
Identify the basic information found on an MSDS, and relate this information to specific precautions.
-
Describe their role and responsibility regarding procedures that help maintain a safe work environment.

A comprehensive interactive multimedia learning program with certification intended for electronic operators, technicians, and engineers, who work with and around lasers.
Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
-
Understand light as energy and energy conversion.
-
Name the types of injuries that can occur.
-
Describe and identify laser classifications and warning labels.
-
Explain concepts related to the Nominal Hazard Zone.
-
Identify the structure of the eye and relate the structure to the potential for accidental exposure and injury.
-
Describe the concept of Maximum Permissible Exposure.
-
Describe appropriate safety procedures in the use of laser safety eyewear and clothing.
-
Describe the notion of optical density, wavelength dependencies, selection and handling of laser safety eyewear.
-
Identify correct procedures for placement, lockout and tagout, barriers and traps, and hazardous materials.

Employees in any company involved in a business that includes defense articles or services must have an understanding of - and comply with - U.S. Export Controls requirements including the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). This course describes the function and purpose of each of these within the company.

Employees in any company in Canada involved in a business that includes defense articles or services must have an understanding of - and comply with - the requirements of the Controlled Goods Program (CGP) and Canadian Export Controls. This course describes the function and purpose of each of these within the company.

This RF training course is an interactive multimedia eLearning program intended for anyone working in the area of radio frequency communications who requires a basic understanding of RF fundamentals.
Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
- Describe the benefits of "Going Lean".
- Recognize why every organization isn't Lean.
- Compare the attitudes and metrics of Lean with those of traditional organizations, and identify some of the obstacles to transformation.
- Recognize the obstacles you must overcome to become a truly lean organization.

Participants successfully completing this course will be able to:
- Define Value Stream and explain Enterprise Value Stream Mapping and why it is important
- Identify how and where to begin mapping the current value stream
- Describe the development of a Future-State Value Stream Map
- Describe how to develop a Future State Implementation Plan

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
- Describe preparation for a Kaizen event.
- Describe the parts and functions of a Kaizen team.
- Describe the first five steps in the Kaizen Event Process.
- Describe the implement, evaluate, standardize and celebrate steps of the Kaizen process.

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
- Describe Lean as a total system driven systematically by goals and vision.
- Explain the role of Management in Lean implementation via cycles of activity guided by Hoshin or PDCA.
- Describe the role, structure, and purpose of charter documents.
- Describe the typical attributes of a Charter Document and how it relates to Kaizens of differing complexity.
- Describe the use of the A3 chart and compare/contrast its primary characteristics to a simple Kaizen Charter.
- Explain the analysis and planning components of an A3.
- Explain the value of A3 for reporting results.

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
- Describe the benefits and implementation of 5S.
- Describe the benefits and implementation of the "Sort Phase".
- Describe the benefits and implementation of the "Set in Order" phase.
- Describe the benefits and implementation of the "Shine Phase".
- Describe the benefits and implementation of the "Standardize Phase".
- Describe the benefits and implementation of the "Sustain Phase".

Participants successfully completing the program will be able to:
- Explain the basic concepts behind Mistake Proofing.
- Describe the key characteristics of mistake proofing and fail-safing methods and devices.
- Describe the process for implementing mistake proofing.
- Recognize examples of how mistake proofing has been applied.
The objectives of this course are for the participant to:
- Describe the key concepts of flow, including the relationship of flow to value from the customer perspective, customer demand, takt time, variable demand, flow vs push, and issues that prevent flow.
- Explain how flow within the value stream is analyzed, including the role of the EVSM process, identifying process steps and work elements, data gathering and analysis.
- Describe the steps to remove blockages to flow including workplace organization, motion and transport, change-over/turnover, error proofing, over processing, and attention to people skills.
- Explain the steps to improve layout for flow.
- Describe methods for balancing work and facilitating flow.

Lean is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, and is focused on customer demand and customer value. Those working in a lean production system need to understand the Lean tools that are available and recognize how they are used to address specific issues within the total system. The course provides a brief overview of the Lean tools used for planning, stability, continuous flow, synchronous flow and production leveling.